2021. 6. 3. 13:56ㆍ베이지안 딥러닝
Weight space view

위는 bayesian이 아님.
Bayesian은 prior가 생김.
Bayesian은 찾고싶은 parameter(=weight = $w$ )에 대해 prior distribution을 주는 것.
Prior는 $w$ 가 주어졌을때, $y$ 의 확률분포를 구하는 것.
Posterior : 데이터가 있을 때, $w$ parameter에 대한 확률
Conjugate prior
Prior distribution에 많이 쓰는 것 : 뤼샤츠, 데이타, 감마, 가우시안(이게 아니면 posterior를 analytic하게 쓸수 없음)
posterior를 analytic하게 쓸수 있으면, 그때의 prior를 conjugate prior라고 부름

Bayesian은 새로운 데이터가 들어왔을때, posterior mean을 구해야 한다
posterior mean = mean over posterior $w$ :
$$E_{w|X,y} [p(f*|x*,w)]$$

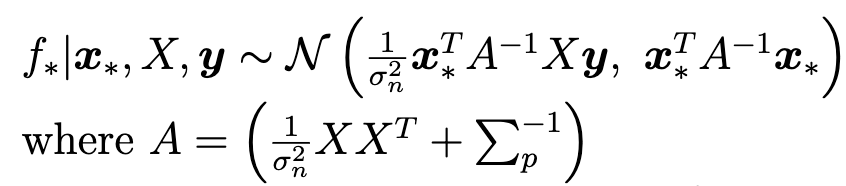
이 위까지는 Gaussian process가 아니다.
Kernel tricks
$$\phi : \mathbb{R}^D \rightarrow \mathbb{R}^N $$ where $x \rightarrow \phi (x).$ : $D$ 차원의 공간을 $N$ 차원의 낮은 차원으로 Embedding
여기서 prior distribution noise term인 $\sigma_n$ 가 존재. ($n$ 개의 prior에 대한 각각의 Gaussian noise)

Function space view
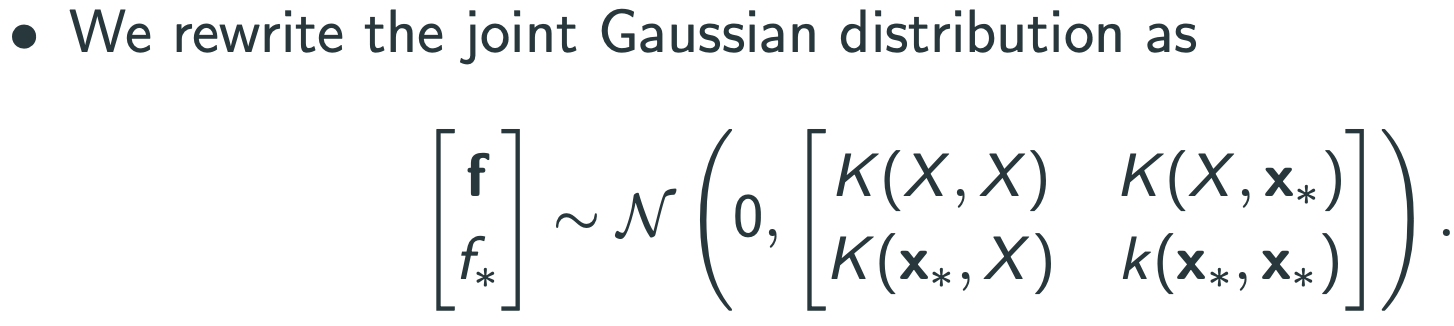

적용 후:
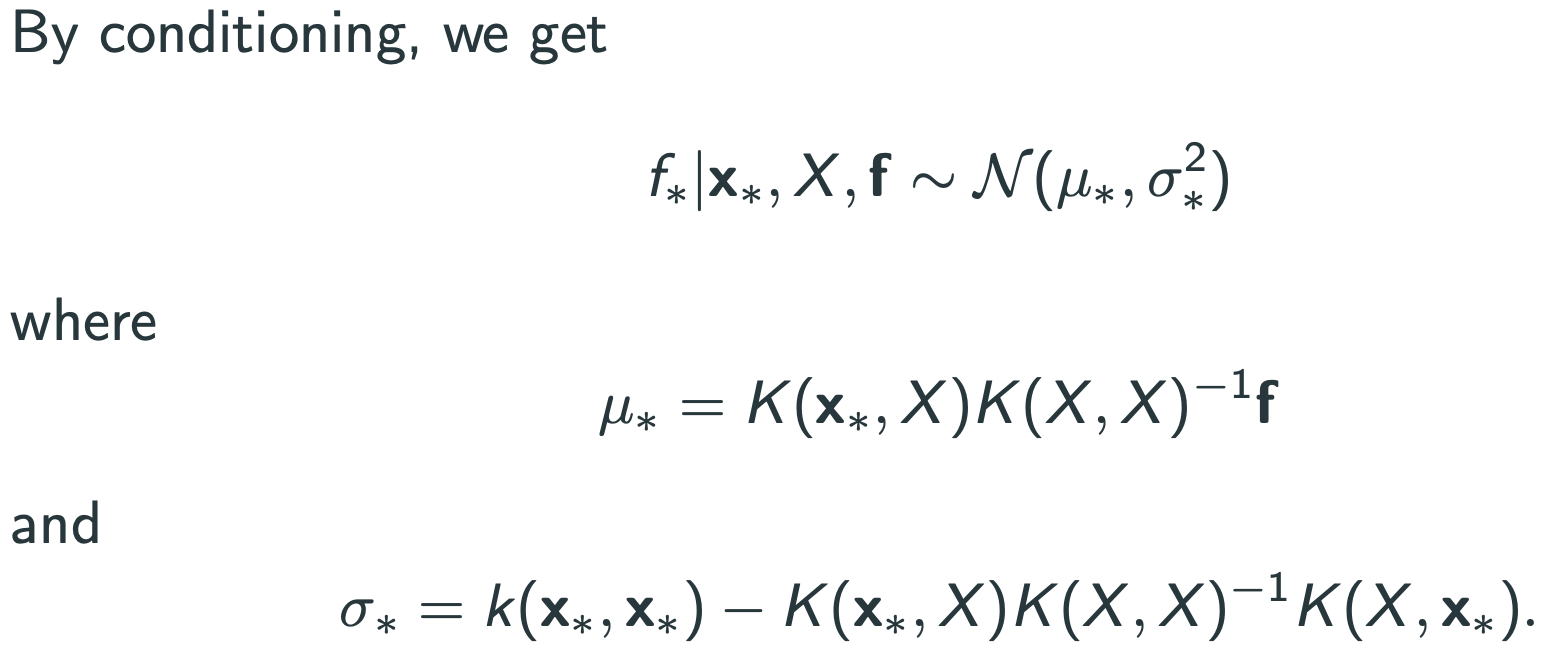
$f$ 에 gaussian 이라는 prior를 두면 bayesian이 됨.
앞에는 measurement noise가 없음.
noise를 넣으면 cov matrix가 바뀜.
$$y = f(x) + \epsilon$$ where $\epsilon \sim \mathcal{N}(0,\sigma^2 _{n})$.
=>
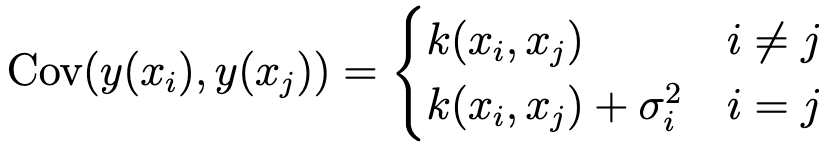
=>
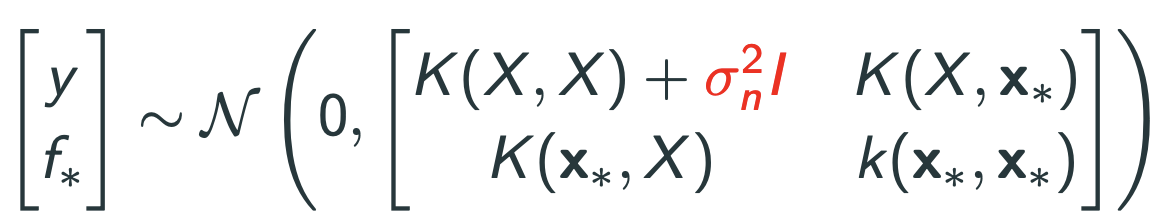
=>
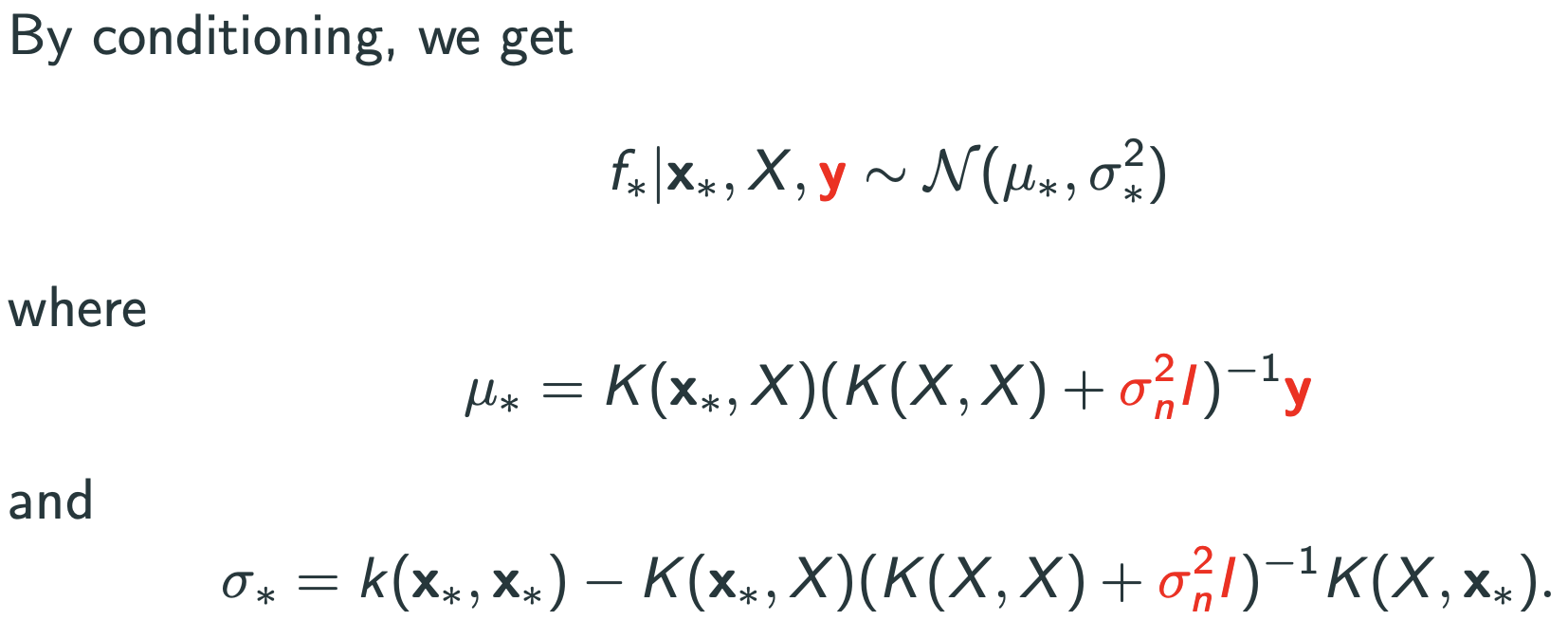
학생 질문 : 왜 nonparameteric method?
mean function을 잘 뜯어보면 representer theorem이 됨.(RKHS조건)
$$\mu_{*}=K(x_{*},X)(K(X,X)+\sigma_{n}^{2}I_{n})^{-1}\overrightarrow{y}=\sum_{i=1}^{n}\alpha_{i}k(x_{i},x_{*})$$ where $\overrightarrow{\alpha}=(K+\sigma_{n}^{2}I_{n})^{-1}\overrightarrow{y}$
이건 Harmonic analysis의 이론처럼 해석 가능하다.
의문점 : Kernel ridge regression이 뭐지?
의문점 : Harmonic analysis 이론이 뭐지?
Gaussian Process Regression에 대한 의견

장점 : 원리적(principled), 확률적(probabilistic), 예측가능한 불확실성(predictive uncertainty)
단점 : 계산량이 많음 = $n \times n$ matrix의 inverse를 계산해야 해서 $O(n^3)$ 임.
'베이지안 딥러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Gaussian process latent variable model(GPLVM) (0) | 2021.06.07 |
|---|---|
| Functional analysis (2) | 2021.05.28 |
| Random process (1) | 2021.05.27 |
| Introduction, Set theory, Measure theory, Probability, Random variable (0) | 2021.05.26 |
